Father of java : James Gosling
First release : May 23 1995 by sun Microsoft
Current owner: oracle corporation from january 2010 to till now
Slogan : write once run anywhere
Used in : Mobile application
Desktop application
Web application
Web server&application
Server
Games
Data base connection etc...
Symbol: coffee cup

Features of java
Features of Java
- Simple
- Robust
- Object- oriented
- Portable
- Platform independent
- Secured
- Architectural neutral
- Interpreted
- High performance
- Multi threaded
- Distributed
- Dynamic
Areas where java is used

Token
A token is the smallest element of a program that is meaningful to the compiler
Token can be divided in many types
- Keyword
- Identifier
- Literals
- Operator
- Separators
- Comments
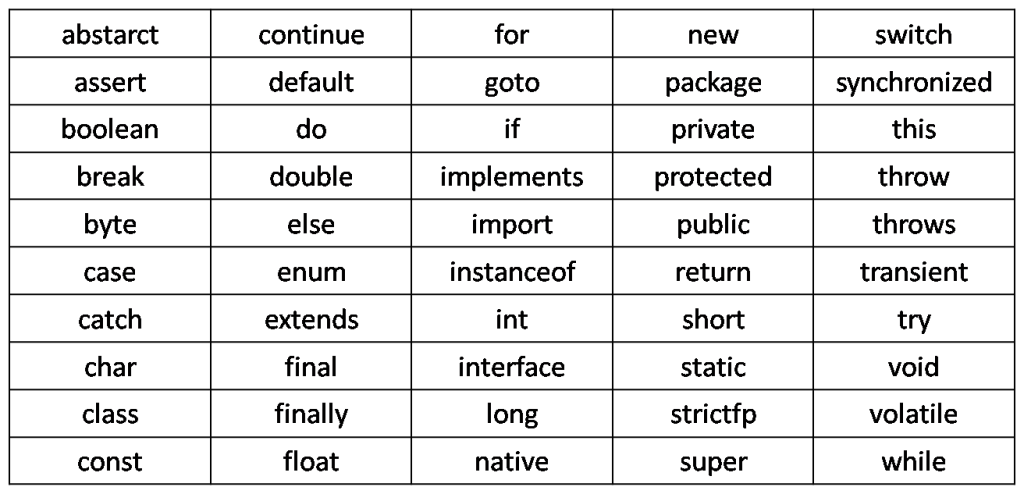
Keyword
- Keyword are predefined
- Keyword are reserve words used in java programming that has special meaning to the compiler
- Every keyword has a specific action to perform
- All keyword are lower in case
- All keyword has one single word
Identifies
A particular name generated by the programmer to define a variable, structure, class, or function is called an identifier
There are some Rules for identifier
- Names can contain letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs.
- Names must begin with a letter.
- Names should start with a lowercase letter and it cannot contain whitespace.
- Names can also begin with $
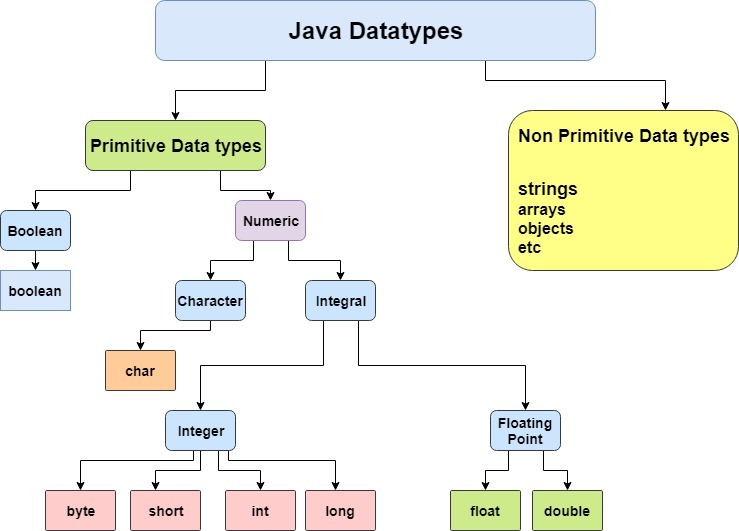
Data types
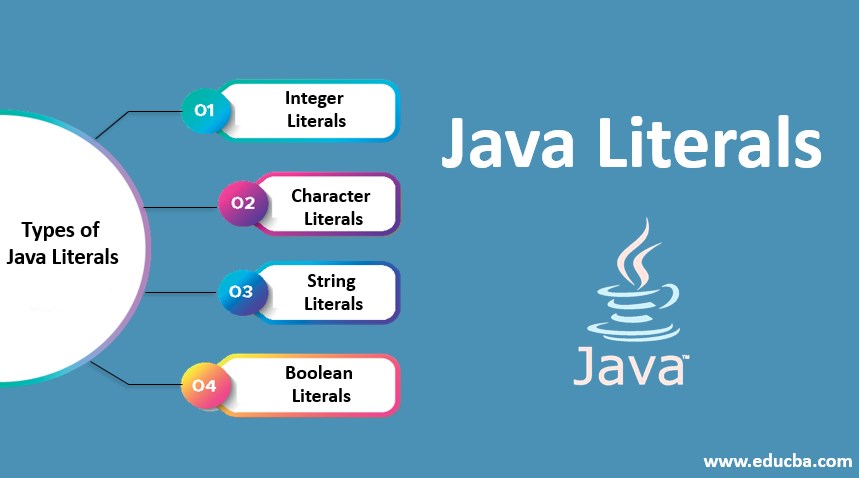
Literals
1.Any constant value which can be assigned to the variable is called literal
2.Literals in Java is a synthetic representation of boolean, numeric, character, or string data
Comments
There are 3 types of comments in java
- Single Line Comment.
- Multi Line Comment.
- Documentation Comment.

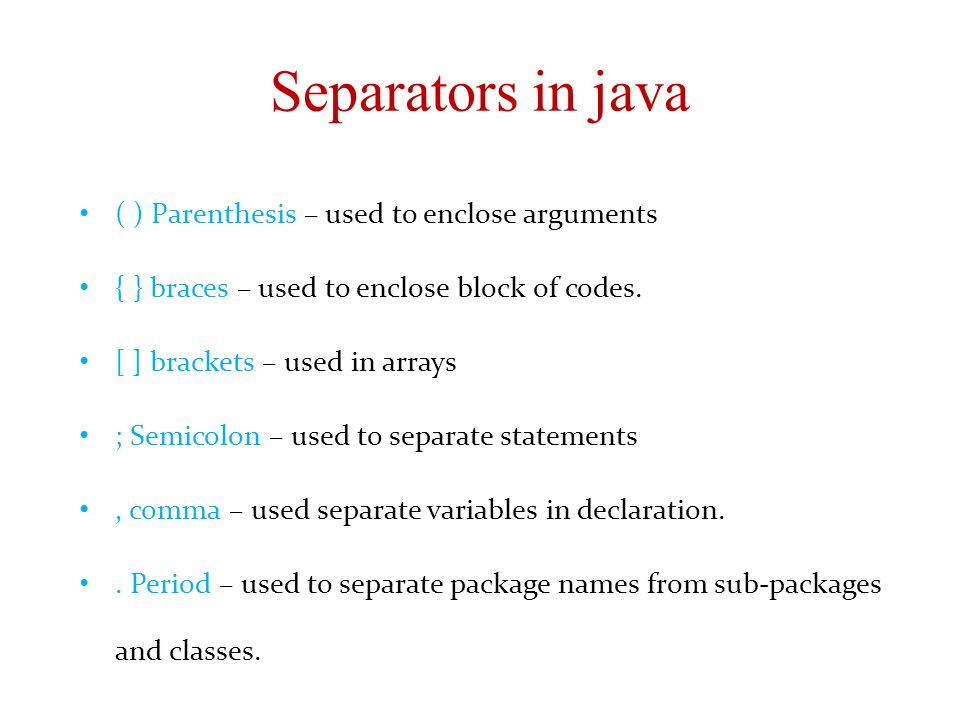
Separators
- Separators helps us to defining the structure of a program in java
a class describes the contents of the objects that belong to it: it describes an aggregate of data fields (called instance variables), and defines the operations (called methods). object: an object is an element (or instance) of a class; objects have the behaviors of their class.
- there are few characters used as separators
Operators
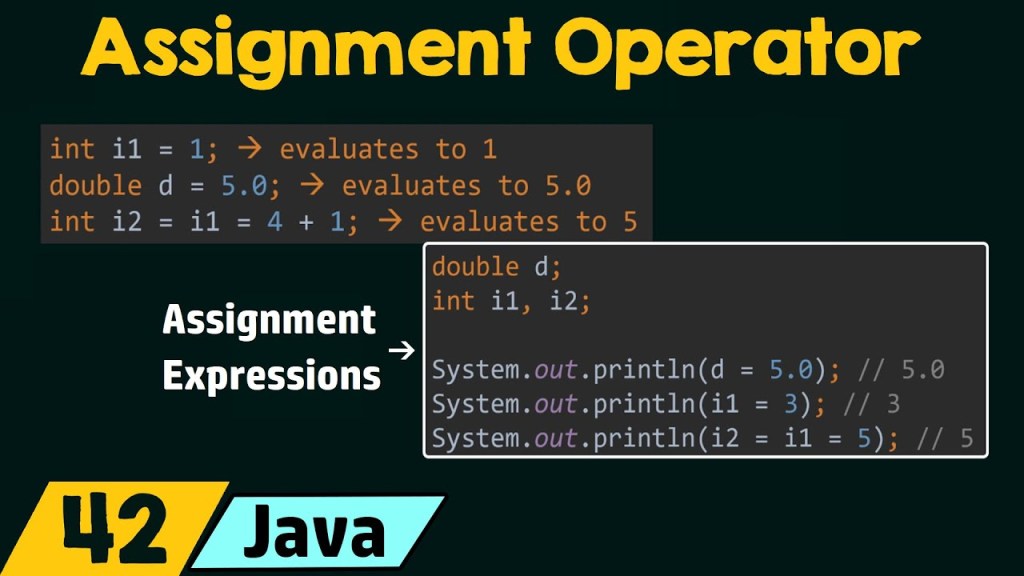
- Operators in java is a symbol that is used to perform operation
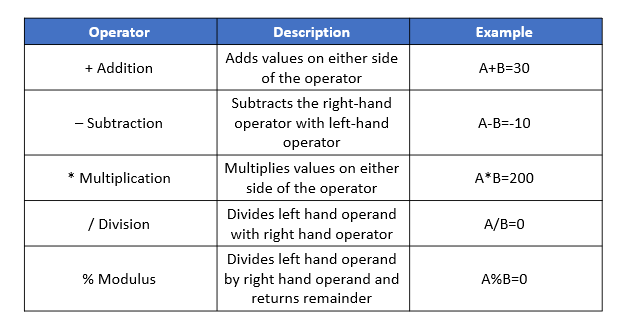
Arithmetic operators
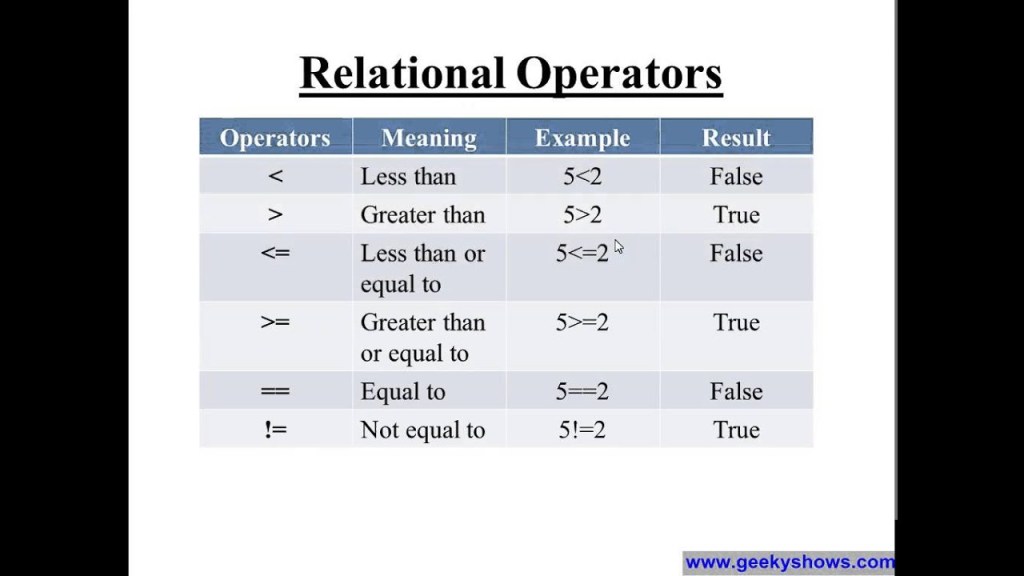
Relational operators
Logical operators

Conditional operators

Assignment operators
Methods
A method in java is a block of code that when called, performs specific actions mentioned in it
Methods are used to preform certain actions and they are also known as functions
All Business logic are implemented write as method in java
Rules for a method
- A method can have any number of inputs (Parametes).
- A method can have only one return value (output).
- Except method with void.
- A variable created inside a method is specific to that method. (cannot be used by other method). This is known as local variable.
- Return should be last line of any method.
- If there is a method name inside a method its called as dependent method.
- Method call should be substituted by return value by the developer.
- pass value as per number of parameters.
Class
A class describe the contents of the object that belong to it. it describes an aggregate of data fields (called instance variables), and defines the operations (called methods). object: an object is an element (or instance) of a class; objects have the behaviors of their class.
- First and foremost topic in oops.
- “Class” is a keyword to create class in java.
- It is a blueprint/template/structure of an object.
- A class can have any number of objects.
- All methods should come inside a class.
- A java file cam have any number of classes but out of all only one should be a main class.
- Java program doesn’t exist without a class.
Object
- it is an oops topic
- object is an instance o a class
- “new” — is a keyword to create object in java
- object executes methods & order of execution is also defined by object
- object has state and behaviour
- class is dummy without an object(class gets life only when we create object)
(object takes he responsibility of method execution)
(method call-- hence called as oops).
object creation syntax:
class-name objectname(identifer)=new(keyword) class-name();
ex:
Arithmetic obj=new Arithmetic
Java control statements
A control statement in java is a a statement that determined whether the other statement will be executed or not. It controls the flow of a program. An ‘if’ statement in java determines the sequence of execution between a set of two statements.
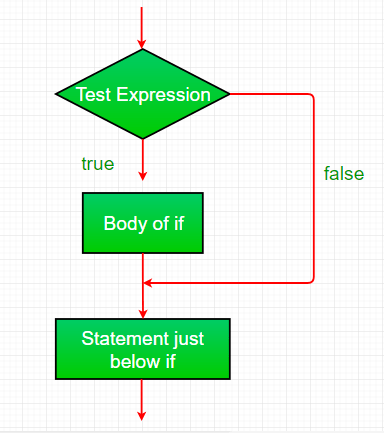
Simple if
If the given condition is true then the statements inside the body of “if” will be executed. If the condition is false then the statements inside the body of “if” will be skippe
If..else statement
If else statement is a condition statement that is used in the execution of a computer program in pre-defined rules. The if-else statement helps you to run a specific block of a program if the condition is true or else, it will check other conditions.

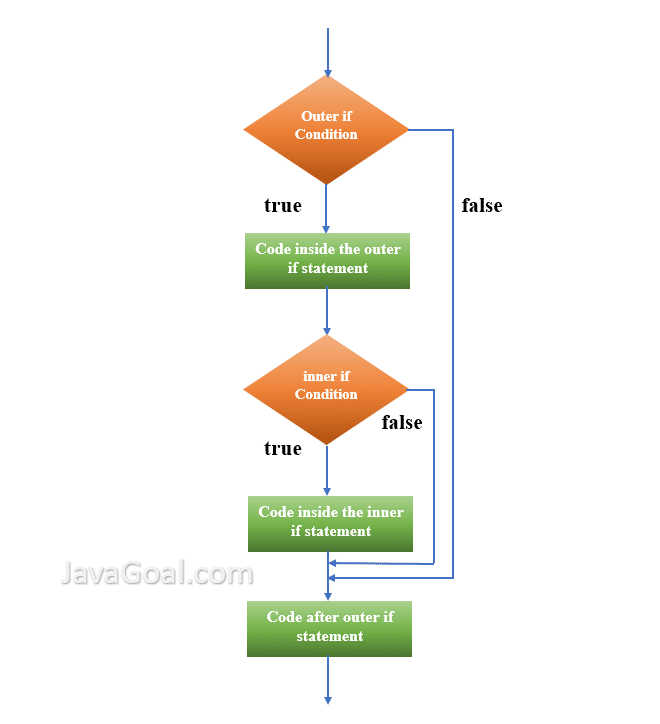
Nested if else
The nested if statement in Java is a set of if conditions one within another. The inner if conditions are only executed when the outer if condition results in true; otherwise the corresponding else block is executed. The nested if condition can also be used with nested if..else statement
Switch case statement
The switch case in java executes one statement from multiple ones. Thus, it is like an if-else-if ladder statement. It works with a lot of data types. The switch statement is used to test the equality of a variable against several values specified in the test cases.
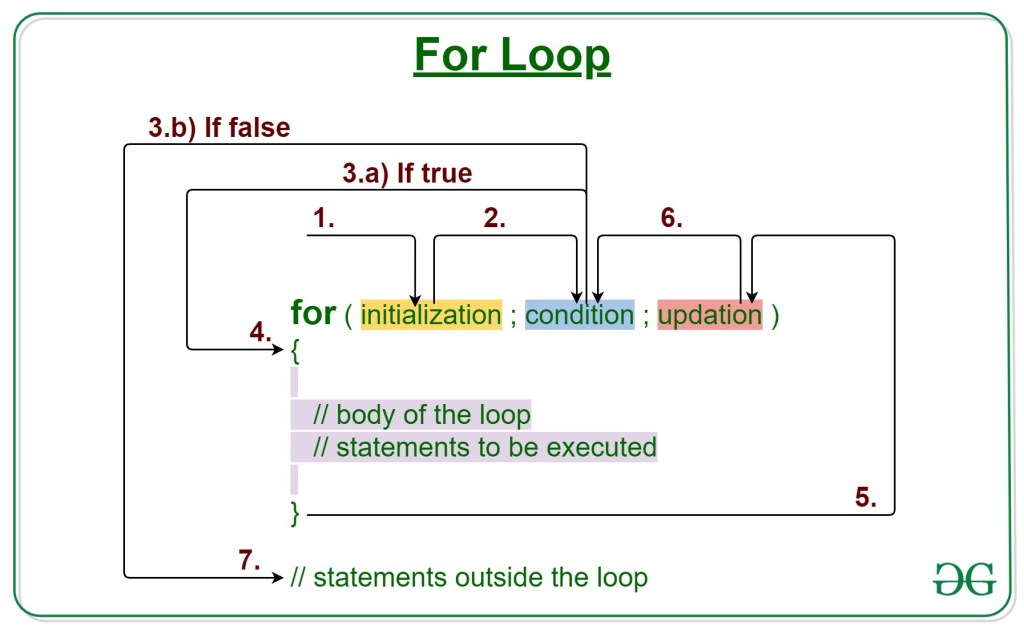
For Looping statement
When you know exactly how many times you want to loop through a block of code, use the for loop
Looping is repeated executed ( something that work again and again
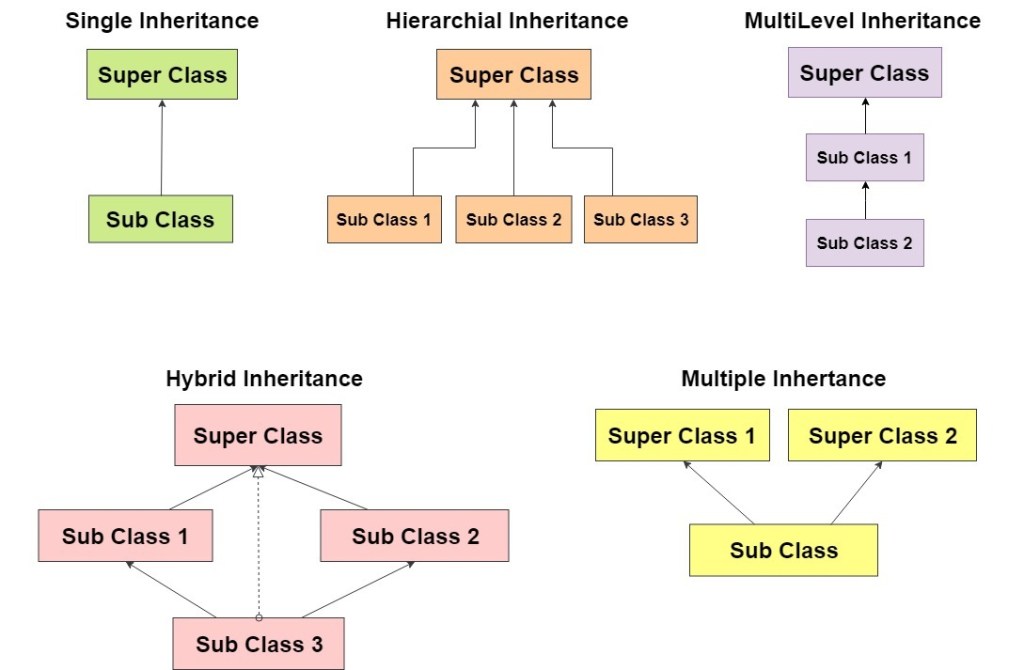
Inheritance
In Java, it is possible to inherit attributes and methods from one class to another. We group the “inheritance concept” into two categories:
- subclass (child) – the class that inherits from another class
- superclass (parent) – the class being inherited from
- Its an OOPs topics.
- It deals with classes.
- Extends is a keyword for inheritance in java.
- A class which gives its properties to another class is called as parent class.
- A class which receivers properties from another classes is called as a child class.
- Transfer of properties (stare and behaviour) takes place in inheritance
Types of inheritance
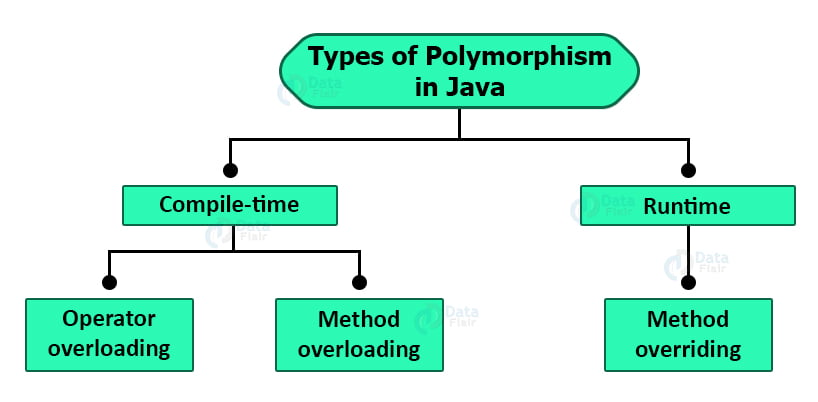
Polymorphism
Poly – many
Morphism-Forms
it occurs when we have many classes that are related to each other by inheritance.
Inheritance lets us inherit attributes and methods from another class.
Polymorphism uses those methods to perform different tasks. types of polymorphism
Types of Polymorphism
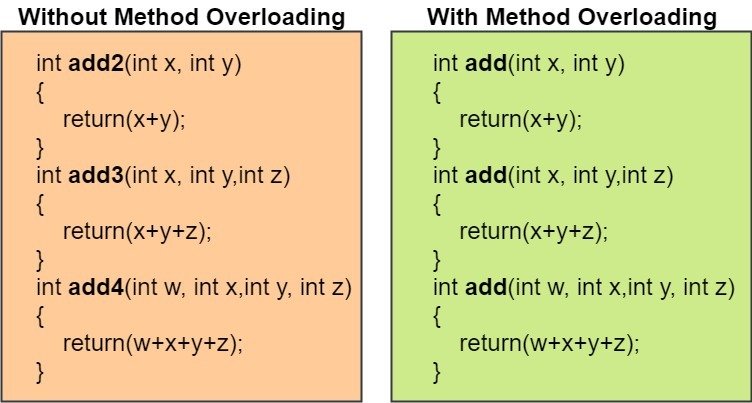
Overloading
a concept of Java in which we can create multiple methods of the same name in the same class, and all methods work in different ways.
within a class /inside a class.
more than one method name are same.
either variable in no.of parameter or type of parameter.
Overriding
method overriding occurs when a subclass (child class) has the same method as the parent class. In other words, method overriding occurs when a subclass provides a particular implementation of a method declared by one of its parent classes.

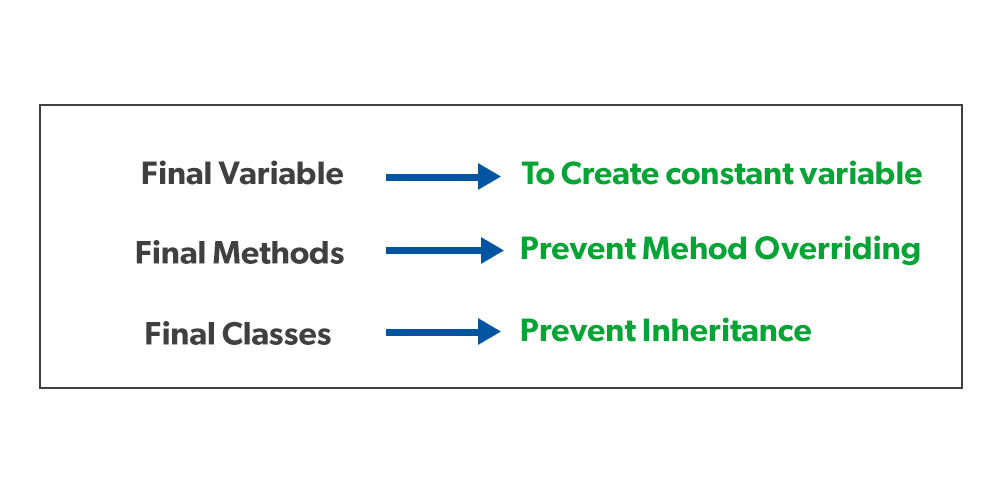
Final keyword in java
- The final keyword is a non-access modifier used for classes, attributes and methods, which makes them non-changeable (impossible to inherit or override).
- The final keyword is useful when you want a variable to always store the same value, like PI (3.14159…).
- The final keyword is called a “modifier”.
Final keyword with variable
1)final is an keyword in java which used for providing code restriction.
final int a=5;
2) It is called data constant
final keyword can be used with variable ,methods,class(using final variable value can't change)
assignment operator will be disabled if we use final keyword for this variable,which means we can't reassign the value.
doing so will result in compile error...
Final keyword with class
- final class cant be extended that is cant be a parent class or it cant have a child class
- This is class restrict inheritance
- It can be child class but it cant have a child class
Final keyword with Methods
Final method cannot be overridden , final method definitely will get inherited. Overriding in final method will result in compiler error
Break & continue
Break
Break: The break statement in java is used to terminate from the loop immediately. When a break statement is encountered inside a loop, the loop iteration stops there, and control returns from the loop immediately to the first statement after the loop.

Continue
The continue keyword is used to end the current iteration in a for loop (or a while loop), and continues to the next iteration.

Constructor
Constructor in java is used to create the instance of the class. Constructors are almost similar to methods except for two things – its name is the same as the class name and it has no return type. Sometimes constructors are also referred to as special methods to initialize an object.